How Liquid AI’s LFM2.5 Brings Foundation Models to On-Device AI Agents
As AI systems move from cloud-only deployments toward on-device and edge execution, model design priorities are changing. Latency, memory footprint, power efficiency, and deterministic performance now matter as much as raw benchmark accuracy. Large foundation models excel in centralized environments, but they are poorly suited for phones, embedded systems, robotics, and private local agents.
Liquid AI’s release of LFM2.5 directly addresses this gap. LFM2.5 is a new generation of compact foundation models designed specifically for real on-device agents, combining strong reasoning capabilities with architectures optimized for CPUs, NPUs, and constrained hardware. Rather than shrinking a large model after training, Liquid AI built LFM2.5 from the ground up for local execution.
This article explores what LFM2.5 is, how it is architected, how it compares to other small open models, and why it represents an important step forward for edge AI systems.
Why On-Device AI Needs a Different Design Philosophy
Most modern language models are trained and deployed with cloud inference in mind. Even smaller variants often assume access to GPUs, large memory pools, and elastic compute. When deployed on-device, these models face several challenges:
- High latency due to memory access and inefficient compute graphs
- Power consumption that exceeds mobile or embedded budgets
- Limited concurrency and poor responsiveness for interactive agents
- Privacy concerns when data must leave the device
On-device agents, such as personal assistants, offline copilots, and embedded reasoning systems, require fast, predictable inference and tight memory control. LFM2.5 targets this exact operational space.
Overview of the LFM2.5 Model Family
LFM2.5 is built on Liquid AI’s LFM2 architecture and centers around a 1.2 billion parameter backbone. The family includes multiple specialized variants, all released as open weights on Hugging Face and accessible through Liquid AI’s LEAP platform.
The released variants include:
- LFM2.5-1.2B-Base for general-purpose inference
- LFM2.5-1.2B-Instruct optimized for instruction following and tool use
- LFM2.5-1.2B-JP optimized for Japanese language tasks
- LFM2.5-VL-1.6B for vision language workloads
- LFM2.5-Audio-1.5B for native audio-to-audio interactions
This breadth signals a clear intention. LFM2.5 is not a single model but a device-first foundation model ecosystem.
Architecture Built for Device Efficiency
At the architectural level, LFM2.5 retains the hybrid LFM2 design, which was created specifically to optimize inference on CPUs and NPUs rather than relying on GPU-centric assumptions.
Key architectural goals include:
- Reduced memory bandwidth pressure
- Efficient execution on low-power accelerators
- Stable performance across heterogeneous hardware
Instead of focusing solely on transformer scaling laws, Liquid AI emphasizes execution efficiency per parameter, which is critical for real-world edge deployments.
Expanded Pretraining and Post-Training Pipeline
One of the major improvements in LFM2.5 over its predecessor is the scale of pretraining data. The 1.2B backbone is pretrained on 28 trillion tokens, up from 10 trillion tokens in earlier versions.
For the instruct model, Liquid AI applies a multi-stage post-training pipeline that includes:
- Supervised fine-tuning
- Preference alignment
- Large-scale reinforcement learning
- Tool use and instruction following optimization
This combination allows LFM2.5-1.2B-Instruct to punch above its weight in reasoning, math, and structured outputs, despite its compact size.
Text Model Performance at the 1B Scale
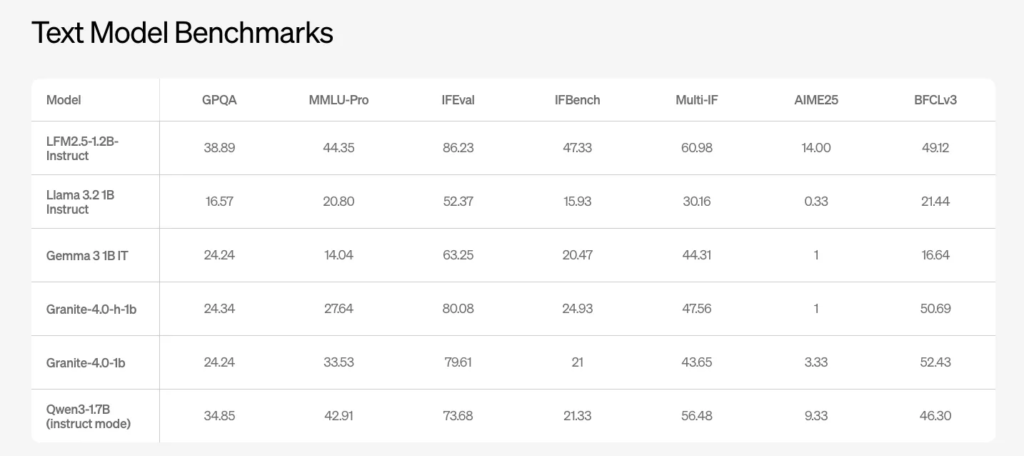
The flagship general-purpose model is LFM2.5-1.2B-Instruct. Liquid AI reports benchmark results across a range of reasoning and instruction-following evaluations, including GPQA, MMLU Pro, IFEval, and IFBench.
Reported scores include:
- 38.89 on GPQA
- 44.35 on MMLU Pro
- 86.23 on IFEval
- 47.33 on IFBench
At the one-billion-parameter scale, these results outperform or match competing open models such as Llama 3.2 1B Instruct and Gemma 3 1B IT on instruction-following and function-calling tasks.
For developers building local agents, this means stronger reasoning and more reliable structured outputs without needing cloud inference.
Japanese-Optimized Variant for Regional Workloads
LFM2.5 also includes LFM2.5-1.2B-JP, a Japanese-optimized text model derived from the same backbone. This variant is tuned specifically for Japanese benchmarks such as JMMLU, Japanese GSM8K, and localized instruction-following tasks.
On these benchmarks, the JP variant competes with or surpasses larger multilingual models, including Qwen3-1.7B and Llama 3.2 1B Instruct. This highlights the value of region-specific optimization when deploying AI agents on-device in global markets.
Vision Language Model for Edge Multimodal Tasks
For multimodal applications, Liquid AI released LFM2.5-VL-1.6B, which pairs the 1.2B language backbone with a vision encoder.
This model is tuned on a wide range of benchmarks, including:
- OCRBench v2
- InfoVQA
- MMStar
- RealWorldQA
- MMMU
- Multilingual MMBench
Compared to its predecessor, LFM2.5-VL-1.6B shows consistent improvements and is designed for real-world edge tasks such as document understanding, UI parsing, and visual reasoning on-device.
Native Audio Language Model with Real-Time Focus
Perhaps the most distinctive member of the family is LFM2.5-Audio-1.5B, a native audio language model that supports both text and audio inputs and outputs.
Unlike cascaded ASR and TTS systems, this model operates in an audio-to-audio paradigm. It introduces a new audio detokenizer that Liquid AI reports as eight times faster than previous Mimi-based approaches at the same precision.
The model supports two generation modes:
- Interleaved generation for real-time speech-to-speech agents
- Sequential generation for ASR and TTS tasks without reinitialization
Quantization-aware training ensures that speech quality metrics such as STOI and UTMOS remain close to full-precision baselines, enabling deployment on constrained hardware.
Open Weights and Deployment Flexibility
All LFM2.5 models are released as open weights, allowing developers to:
- Self-host models locally
- Fine-tune for domain-specific tasks
- Profile and optimize inference pipelines
- Deploy without vendor lock-in
This openness is especially important for on-device AI, where privacy, offline capability, and long-term maintainability are often non-negotiable requirements.

Why LFM2.5 Matters for On-Device Agents
LFM2.5 represents a clear departure from the idea that on-device AI is merely a compressed version of cloud AI. Instead, it treats device constraints as design inputs, not limitations.
Key takeaways include:
- Strong reasoning at the 1B parameter scale is achievable with the right training recipe
- Hybrid architectures can outperform larger transformer-only models in edge settings
- Multimodal and audio-native agents can run locally with acceptable latency
- Open, specialized models unlock real-world adoption beyond the cloud
As AI agents increasingly run on phones, wearables, robots, and embedded systems, model families like LFM2.5 will likely define the next phase of applied AI.
Conclusion
Liquid AI’s release of LFM2.5 signals a maturing view of AI deployment. Rather than chasing ever-larger models, it focuses on usable intelligence under real-world constraints. With strong text reasoning, multimodal support, native audio capabilities, and open deployment, LFM2.5 provides a compelling foundation for truly local AI agents.
For teams building privacy-preserving, low-latency, and power-efficient AI systems, LFM2.5 is not just another small model. It is a blueprint for what on-device foundation models can become.
Check out the technical details and model weights. All credit for this news goes to the researchers of this project. Explore one of the largest MCP directories created by AI Toolhouse, containing over 4500+ MCP Servers: AI Toolhouse MCP Servers Directory