Meta AI introduces SPIRIT-LM: A Foundation Multimodal Language Model that Freely Mixes Text and Speech
In the field of Natural Language Processing (NLP), the development of large language models (LLMs) has revolutionized the way machines understand and generate human language. These models, such as GPT-3, have enabled significant advancements in various NLP tasks. However, as the focus shifts towards multimodal communication, Meta AI has introduced a groundbreaking model called SPIRIT-LM. This multimodal language model seamlessly integrates text and speech, opening up new possibilities for enhanced human-machine interactions.
🔥Explore 3500+ AI Tools and 2000+ GPTs at AI Toolhouse
SPIRIT-LM: A Revolutionary Approach to Multimodal Communication
SPIRIT-LM is a foundational multimodal language model developed by Meta AI. It builds upon pre-existing text language models and expands their capabilities to incorporate speech. This integration of both modalities allows SPIRIT-LM to freely mix text and speech, enabling more comprehensive language understanding and generation1.
Two Variants, One Goal
SPIRIT-LM is available in two distinct variants: the BASE version and the EXPRESSIVE version. The BASE version employs speech semantic units to encode spoken language, while the EXPRESSIVE version goes a step further by incorporating pitch and style units to capture expressive qualities in addition to semantic understanding1.
Both variants utilize subword BPE tokens to encode textual inputs. This tokenization process enables the model to handle a wide range of linguistic patterns and structures effectively. By combining the semantic comprehension of text models with the expressive qualities of speech models, SPIRIT-LM achieves a more holistic understanding of multimodal communication.
Training and Architecture
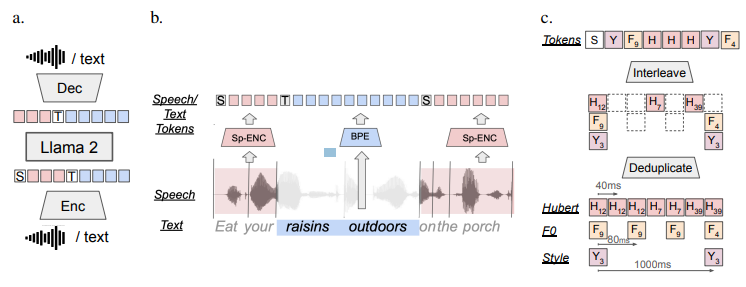
The architecture of SPIRIT-LM revolves around a language model that is trained through next-token prediction. This process involves generating tokens from either speech or text inputs using an encoder-decoder framework. During training, the model is exposed to a combination of text-only sequences, speech-only sequences, and interleaved speech-text sequences.
The training of SPIRIT-LM incorporates a unique approach to integrating speech and text. Speech is encoded into tokens using clusterized speech units, such as Hubert, Pitch, or Style tokens, while text is encoded using byte-pair encoding (BPE). Special tokens, [TEXT] for text and [SPEECH] for speech, mark the respective modality. Interleaving occurs at word boundaries within aligned speech-text corpora, allowing for a seamless integration of the two modalities1.
To further enhance expressivity, SPIRIT-LM-EXPRESSIVE introduces pitch and style tokens. These tokens, interleaved after deduplication, enrich the model’s ability to capture nuances in speech delivery and tone.
The Implications of SPIRIT-LM
The introduction of SPIRIT-LM paves the way for significant advancements in various fields that leverage natural language understanding systems. Here are a few areas that stand to benefit from this multimodal language model:
Conversational Agents and Virtual Assistants
Conversational agents and virtual assistants play a crucial role in human-computer interactions. With the integration of text and speech in SPIRIT-LM, these agents can better understand and generate natural language. This leads to more seamless and lifelike conversations, enhancing user experience and satisfaction2.
Language Translation
Language translation is a complex task that requires understanding and generating text in different languages. SPIRIT-LM’s ability to freely mix text and speech can greatly improve translation accuracy and fluency. By incorporating speech inputs, the model gains access to additional contextual cues, resulting in more accurate translations3.
Accessibility Tools
For individuals with speech or hearing impairments, communication can be a challenge. SPIRIT-LM opens up new possibilities for accessibility tools by enabling bidirectional communication between text and speech. These tools can assist individuals in transcribing speech to text or synthesizing speech from text, breaking down barriers and promoting inclusivity.
The Future of Multimodal Language Models
SPIRIT-LM is just the beginning of a new era in multimodal communication. As research and development in large language models and speech-language models continue to evolve, we can expect further advancements in the field. Innovations in prompt creation and model design will contribute to even more sophisticated language understanding systems, pushing the boundaries of human-machine interactions.
With Meta AI’s SPIRIT-LM and similar future models, the synergy between text and speech will unlock exciting possibilities across various domains. Whether it’s conversational agents, language translation, or accessibility tools, multimodal language models have the potential to revolutionize how we interact with technology and bridge the gap between humans and machines.
In conclusion, Meta AI’s SPIRIT-LM introduces a foundation multimodal language model that seamlessly integrates text and speech. With its two variants, BASE and EXPRESSIVE, SPIRIT-LM combines the strengths of text and speech models to achieve a more comprehensive understanding of multimodal communication. This breakthrough has far-reaching implications for fields such as conversational agents, language translation, and accessibility tools. As the development of multimodal language models advances, we can look forward to more lifelike and engaging interactions between humans and machines.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on LinkedIn. Do join our active AI community on Discord.
If you like our work, you will love our Newsletter 📰