MaLA-500: Revolutionizing Language Models with Unprecedented Language Coverage
Language models have revolutionized the field of Natural Language Processing (NLP) by enabling machines to comprehend and generate human language. These large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated exceptional performance in English and a few other widely spoken languages. However, when it comes to non-English languages, especially those with limited resources, LLMs face significant challenges. The need to bridge this gap has led to the development of MaLA-500, a novel large language model designed to cover an extensive range of 534 languages.
The Challenge of Language Coverage in LLMs
Existing language models, such as XLM-R, have made significant strides in language coverage, but they still fall short in adequately representing the linguistic diversity of the world. The XLM-R model, with 278 million parameters, covers languages ranging from 100 to 534. While this is an impressive achievement, the coverage is still limited.
Low-resource languages, which lack extensive textual data for training, are particularly challenging for LLMs. These languages often suffer from data scarcity, vocabulary peculiarities, and linguistic variations. Adapting LLMs to effectively handle such languages requires innovative strategies and approaches.
🔥Explore 3500+ AI Tools and 2000+ GPTs at AI Toolhouse
Introducing MaLA-500: A Breakthrough in Language Model Coverage
To address the limitations of previous efforts, a team of researchers from LMU Munich, Munich Center for Machine Learning, University of Helsinki, Instituto Superior Técnico (Lisbon ELLIS Unit), Instituto de Telecomunicações, and Unbabel has developed MaLA-500. This groundbreaking large language model has been designed to cover an extensive range of 534 languages, surpassing the language coverage of existing models.
MaLA-500 incorporates various language adaptation strategies to improve its contextual and linguistic relevance across multiple languages. With model parameters scaling up to 10 billion, MaLA-500 aims to provide a comprehensive solution for non-English languages, especially those with limited resources.
Vocabulary Expansion and Ongoing Pretraining
One of the key features of MaLA-500 is vocabulary expansion. By expanding the model’s vocabulary, MaLA-500 can better comprehend and generate content in a wider range of languages. This approach significantly enhances the language coverage of the model and contributes to its adaptability.
Additionally, MaLA-500 undergoes ongoing pretraining using the Glot500-c corpora. This continuous training further refines the model’s language understanding capabilities and helps it adapt to diverse linguistic contexts. By leveraging these techniques, MaLA-500 achieves state-of-the-art in-context learning outcomes, outperforming existing open LLMs with comparable or slightly larger model sizes.
Evaluating MaLA-500’s Performance
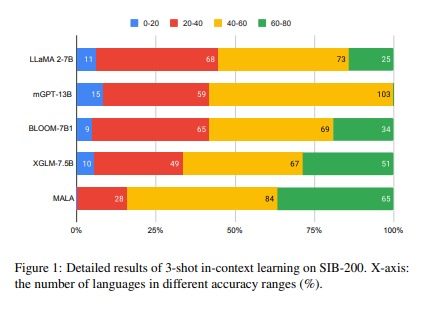
To assess the effectiveness of MaLA-500, the research team conducted an analysis using the SIB-200 dataset. The results demonstrated that MaLA-500 performs exceptionally well in understanding and producing language within specific environments. This highlights the model’s adaptability and its significance in various linguistic contexts.
Comparisons with existing LLMs indicate that MaLA-500 offers superior performance and language coverage. With its innovative approach to vocabulary expansion and ongoing pretraining, MaLA-500 sets a new benchmark in large language models, providing a valuable resource for low-resource languages.
Implications and Future Directions
The development of MaLA-500 holds immense promise for the advancement of language models and their applications. By expanding the accessibility and capabilities of LLMs, MaLA-500 opens up new possibilities for language-specific use cases, particularly those involving low-resource languages. It empowers researchers, developers, and organizations to develop NLP solutions that cater to a broader range of languages and linguistic contexts.
As language technology continues to evolve, future research may focus on further enhancing the language coverage of LLMs like MaLA-500. With advancements in data collection, preprocessing techniques, and model architectures, we can expect even more comprehensive and accurate language models in the years to come.
In conclusion, MaLA-500 represents a significant breakthrough in large language models, addressing the limitations of existing models and expanding language coverage to an unprecedented extent. Its innovative approaches to vocabulary expansion and ongoing pretraining make it a game-changer for low-resource languages. With MaLA-500 leading the way, we can look forward to a future where language technology breaks down barriers and enables effective communication across diverse linguistic landscapes.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on LinkedIn. Do join our active AI community on Discord.
If you like our work, you will love our Newsletter 📰