Improving Speech Recognition on Augmented Reality Glasses with Hybrid Datasets Using Deep Learning: A Simulation-Based Approach
Augmented Reality glasses have revolutionized the way we interact with digital information in the real world. While these devices offer exciting possibilities, there are still challenges to overcome, particularly in the realm of speech recognition. In noisy and reverberant environments, accurately recognizing speech on AR glasses can be difficult. However, recent research has proposed a simulation-based approach that leverages deep learning and hybrid datasets to improve speech recognition performance. This article explores the innovative method and its implications for enhancing communication experiences.
The Challenge of Speech Recognition on AR Glasses
Traditional methods of speech recognition often struggle in noisy and reverberant environments, such as crowded spaces or outdoor settings. Background noise and multiple speakers can hinder the accuracy of speech recognition systems, making it challenging to effectively use AR glasses for communication purposes.
Explore 3600+ latest AI tools at AI Toolhouse 🚀
To address this challenge, researchers at Google AI have developed a novel approach that combines deep learning techniques with hybrid datasets to improve speech recognition on AR glasses. By leveraging simulated data and a joint model combining sound separation and automatic speech recognition (ASR), this approach aims to achieve accurate speech recognition even in challenging acoustic environments.
The Power of Hybrid Datasets
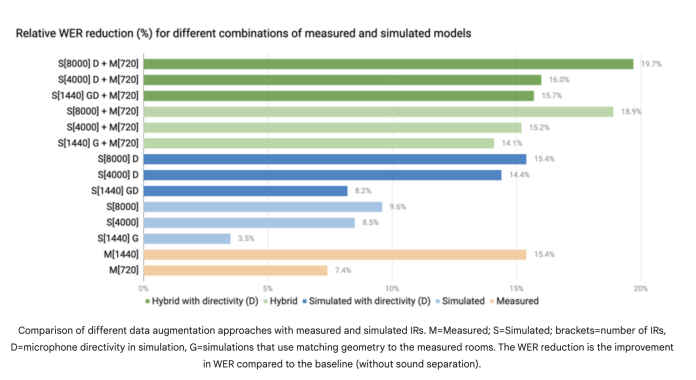
The proposed method involves the use of hybrid datasets, which combine both real-world and simulated acoustic data. This approach harnesses the benefits of both types of data to enhance the performance of speech recognition models on AR glasses.
Simulated data offers several advantages over traditional methods that rely solely on recorded impulse responses (IRs) from actual environments. Collecting real-world IRs can be time-consuming and challenging to scale, whereas simulated data enables the quick and cost-effective generation of diverse acoustics data. By using a room simulator, researchers can generate simulated IRs that capture the unique acoustic properties of AR glasses.
Additionally, the researchers developed a data generation pipeline to synthesize training datasets that include reverberant speech, noise sources, and controlled distributions. This approach ensures that the models trained on the hybrid dataset can accurately handle varying acoustic conditions commonly encountered in real-world scenarios.
Enhancing Model Performance
Experimental results have shown significant improvements in speech recognition performance when using the hybrid dataset compared to using solely real-world or simulated data. The joint model combining sound separation and ASR, trained on the hybrid dataset, outperforms traditional methods in noisy and reverberant environments.

Furthermore, adding microphone directivity in the simulation further enhances the training of the model, reducing the reliance on extensive real-world data collection. The combination of simulated data with device-specific acoustic properties and a joint model approach has the potential to revolutionize speech recognition on AR glasses.
Implications for Communication Experiences
Improving speech recognition on AR glasses has significant implications for communication experiences, particularly for individuals with hearing impairments or those conversing in non-native languages. By enhancing the accuracy and reliability of speech recognition on AR glasses, these devices can become more accessible and effective tools for communication in various settings.
The simulation-based approach presented in this research opens up new possibilities for overcoming the challenges of noisy and reverberant environments. By combining real-world and simulated data, it captures the complex acoustic properties encountered while wearing AR glasses, enabling more robust and accurate speech recognition.
Conclusion
The simulation-based approach utilizing deep learning and hybrid datasets represents a significant step forward in improving speech recognition on AR glasses. By combining the strengths of simulated and real-world data, this method enhances the performance of speech recognition models in challenging acoustic environments.
The implications of this research are far-reaching, offering improved communication experiences for individuals using AR glasses. The ability to accurately recognize speech in noisy and reverberant environments opens up possibilities for augmented reality applications in various industries, including healthcare, education, and entertainment.
As researchers continue to refine and expand upon this approach, the future of speech recognition on AR glasses looks promising. By leveraging advancements in deep learning and the power of hybrid datasets, we can expect further improvements in communication technology and its accessibility to all individuals.
Check out the Paper. All credit for this research goes to the researchers of this project. Also, don’t forget to follow us on LinkedIn. Do join our active AI community on Discord.
If you like our work, you will love our Newsletter 📰